早期数学笔记,大量使用chatGPT辅助,当时不会Tex,直接放图;中英混杂,但是数论基础部分,不再进行整理。
- Basic Knowledge
- Divisibility
- Greatest Common Divisor and Least Common Multiple
- Euclidean Algorithm
- Modular Arithmetic
- 模余公式及证明
- 课堂小问题 Question on ED forum
- 大数求余
- Question:n = abcd is divisible by 9 if and only if the digit sum a + b +c+d is divisible by 9
- Euclidean Algorithm
- Proof multiples of k between n and m (inclusive)(??)
- gcd(m,n)lcm(m,n)=|m||n|
- For m,n ∈ Z, if m > n then gcd(m,n) = gcd(m−n,n)
- How many numbers between 1 and 653 are divisible by 3 or 5?
- Suppose that n is a positive integer. Explain why n and n + 1 are coprime.
- Find the last two digits of $7^{7^{7}}$
- Find the least positive integer n for which 5n % 17 = 16. Hence, evaluate 5200 % 17.
Basic Knowledge

Real Number【R】
-> Rational #【Q】
-> -> 整数【Z】【含 自然数【N】(0不属于自然数)】
-> -> 分数【有限 和 无限循环小数】
-> Irrational # (满足条件1 小数 2 无线不循环)
Natural: {0,1,2,3,4,5,…}
0是自然数
上取整和下取整
乘数
- multiplier
- multiplicator
乘积
product
除数
divisor
被除数
dividend
商
quotient
幂
power
求余
Find the remainder
极坐标
Pol: polar coordinates
直角坐标:
Rec: Rectangular coordinates
带分数:mixed num
integer part + fractional part
假分数(improper fraction):分子>=分母
分子:numerator
分母:denominator
notion:概念,主张
Divisibility
m|n
m divides n if n=k*m for some k
1|n
true
-1|n
true
任何数可以整除0,但是0不能整除任何数字(除非0), 因为任何数的0倍就是0
0|n (only when n=0)
(notice, 0|n is False, just when n=0, it is True)
n|0
True
(Notice, 0 is anything’s product, cause the other multiplier is 0)
n|1
false only when $n=\pm 1$
Greatest Common Divisor and Least Common Multiple
Let m,n ∈ Z
The greatest common divisor of m and n, gcd(m,n), is the
largest positive d ∈ Z such that d|m and d|n.
The least common multiple of m and n, lcm(m,n), is the
smallest positive k ∈ Z such that m|k and n|k.
Exception: gcd(0,0) = lcm(0,n) = lcm(m,0) = 0
gcd(m,n) and lcm(m,n) are always taken as non-negative even if m or n is negative.
gcd和lcm与正负数无关,直接把负号变正号即可。
Fact:
gcd(m,n)*lcm(m,n)=|m|*|n|
对此证明直接搜
gcd(0,n)=n
lcm(0,n)=0
Euclidean Algorithm
大的数字减去小的数字,直到相同
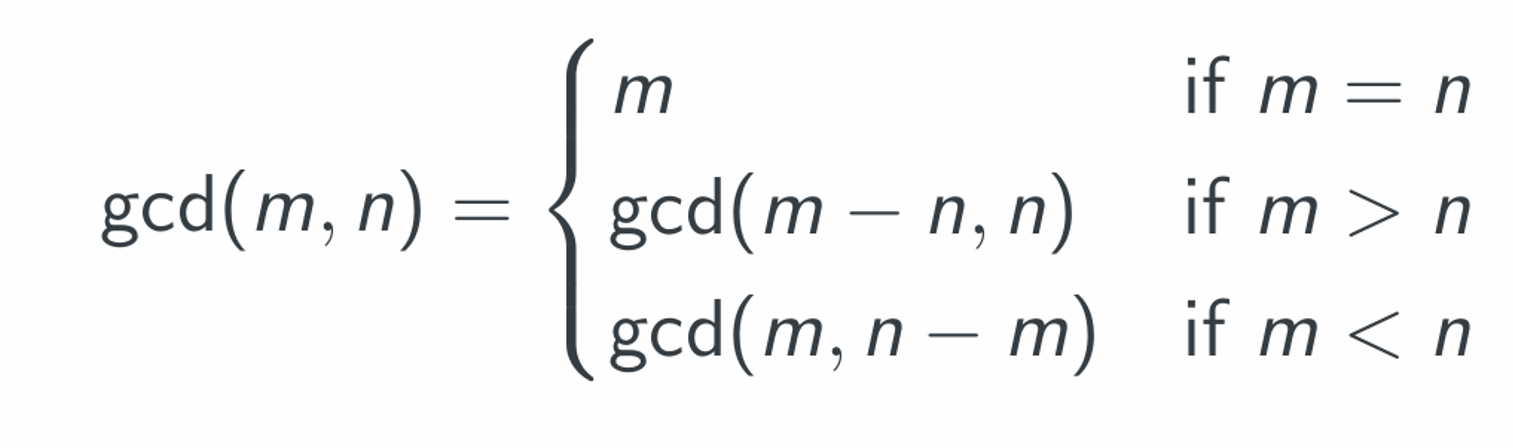
gcd(45,27)=gcd(18,27)=gcd(18,9)=gcd(9,9)=9
gcd(108,8)=gcd(100,8)=gcd(92,8)=…=gcd(4,4)=4
Modular Arithmetic
模运算
4的5次方:4 to the fifth power
For $m ∈ Z, n ∈ \mathbb{Z}_{>0}$ there exists q,r ∈ Z with 0 ≤ r < n
such that
m=q·n+r
Let m,p ∈ Z, n ∈ Z>0.
m div n = $\left\lfloor \frac{m}{n} \right\rfloor$
m % n=m−(mdivn)·n
m=p | mod n if n|(m-p)
模余公式及证明
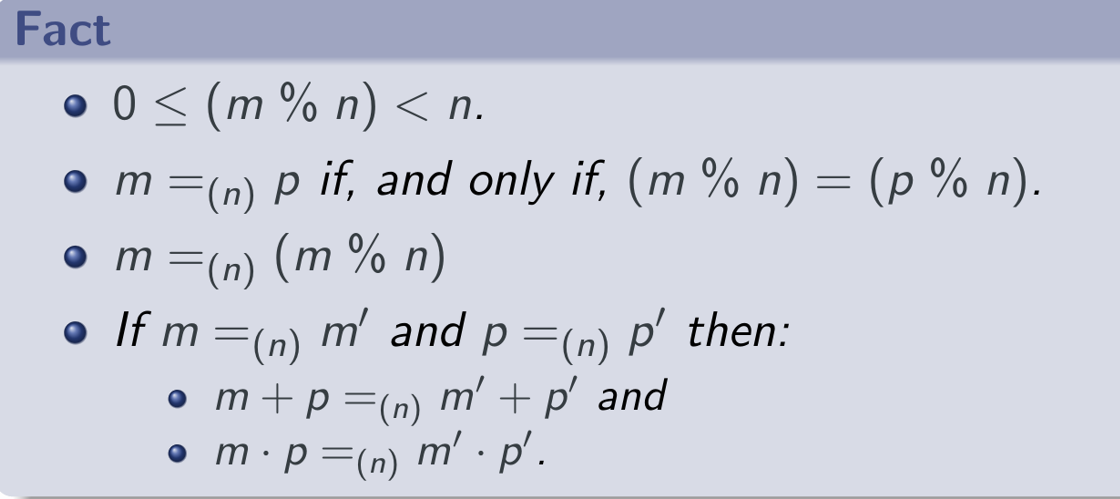
对第二个证明:
proof:
m%n=m-(m div n)*n
p%n=p-(m div n)*n
=>given m=p |mod n
we need to prove m%n=p%n
m%n – p%n = (m-p)-[(m div n) – (p div n)]*n ......(1)
=> n|(1)
对第四个证明:



课堂小问题 Question on ED forum
( a + b ) % n = ( a % n ) + ( b % n)
is False, and you said
( a + b ) % n =(n) ( a % n ) + ( b % n)
IS CORRECT.
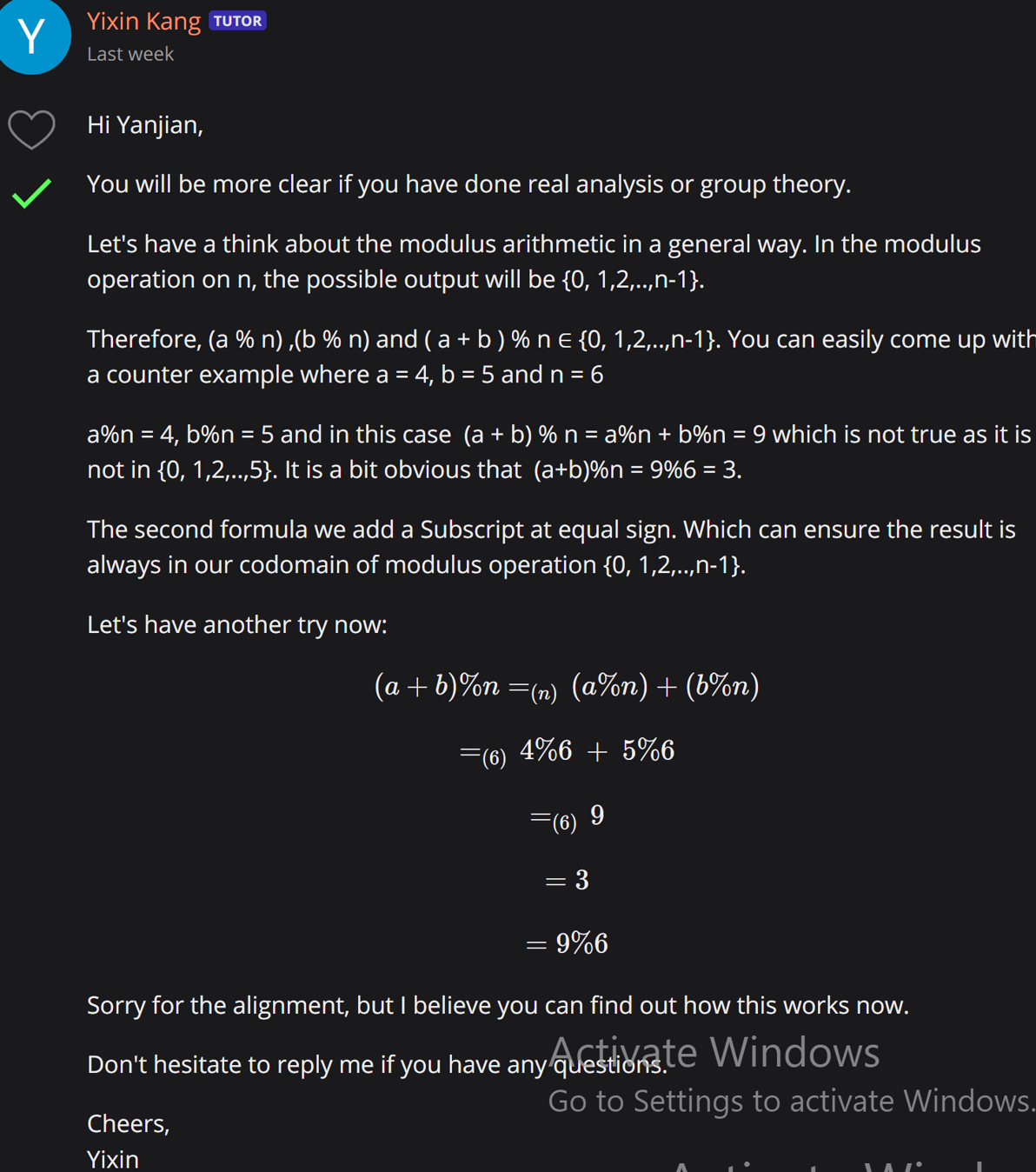
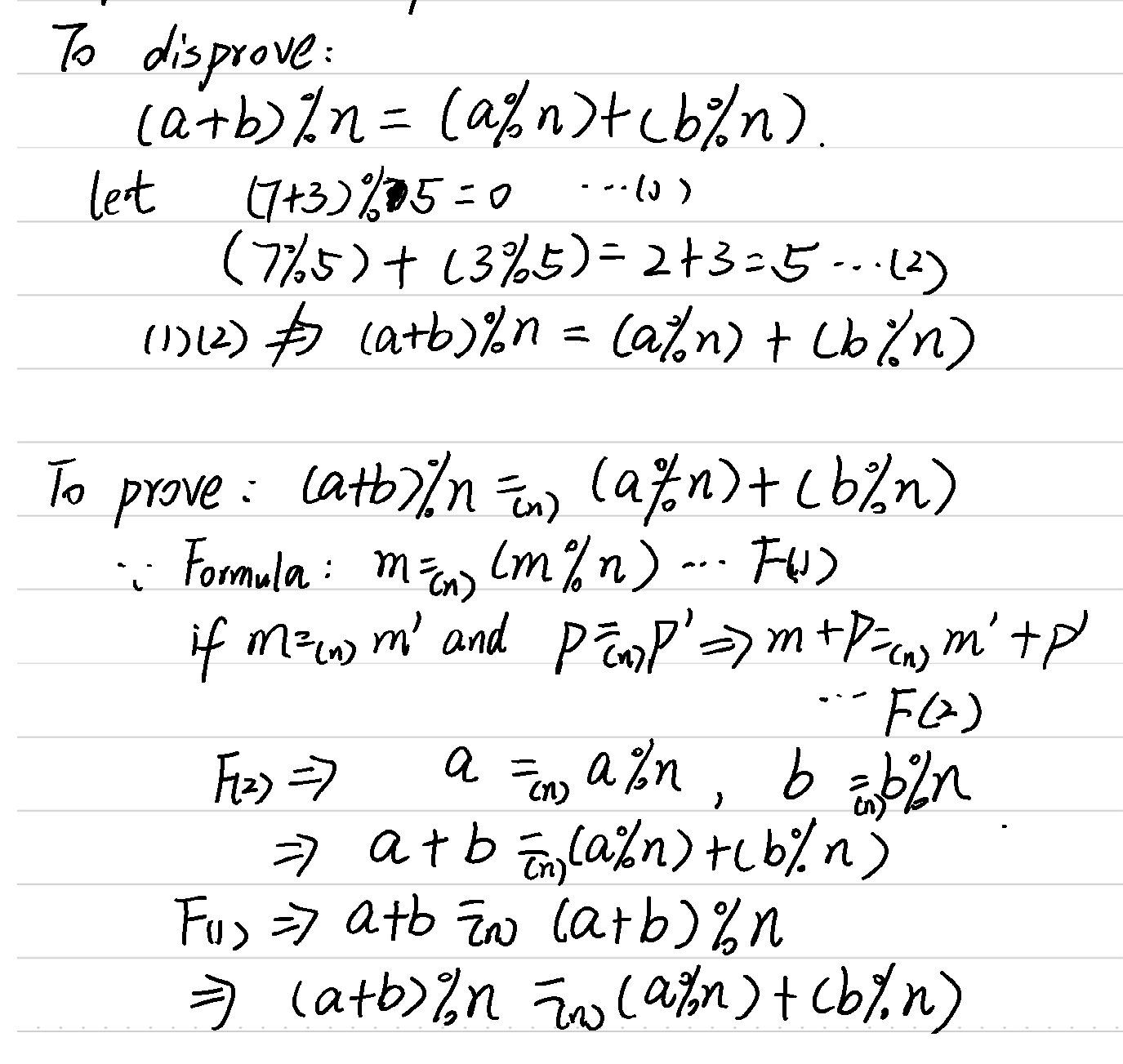
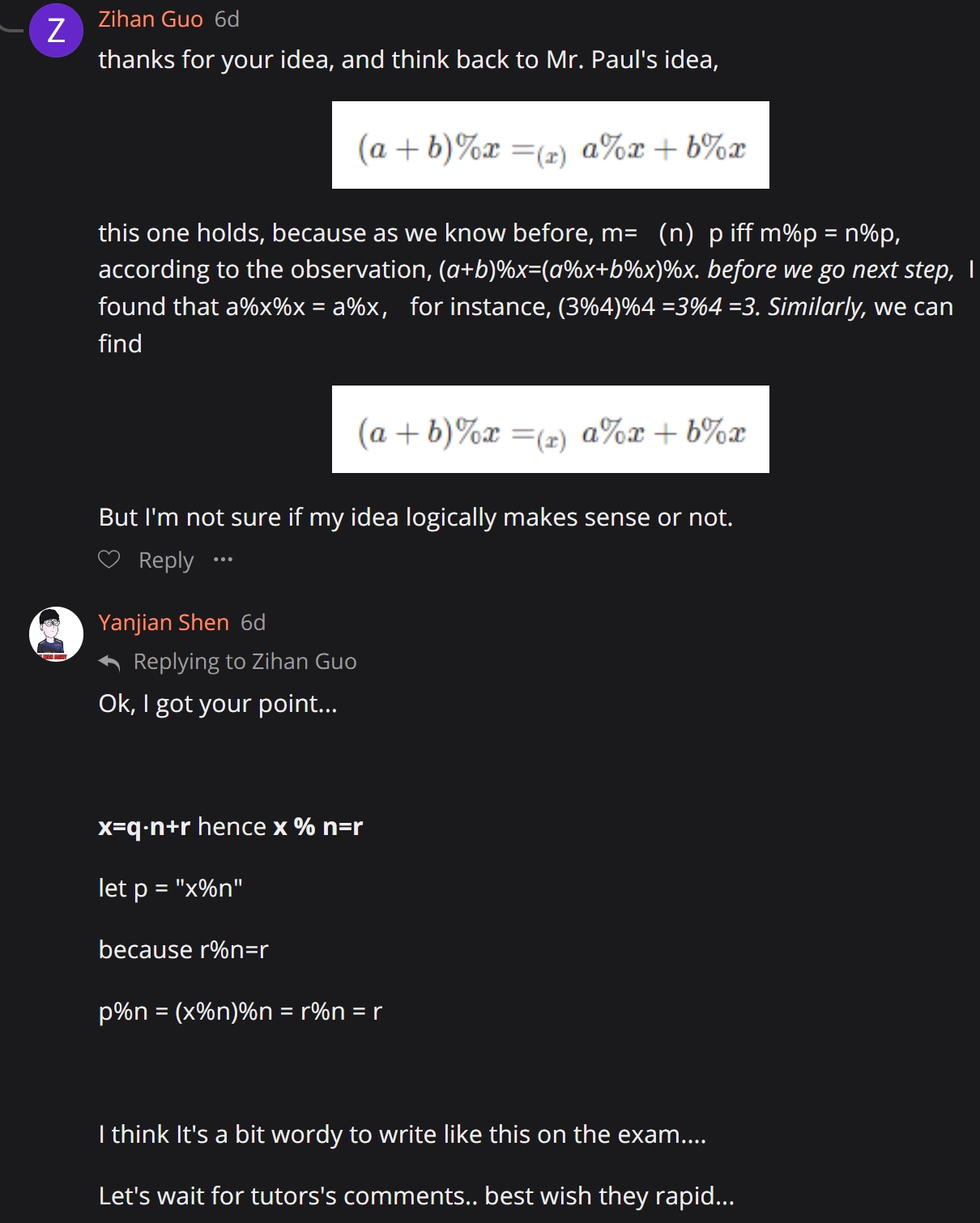
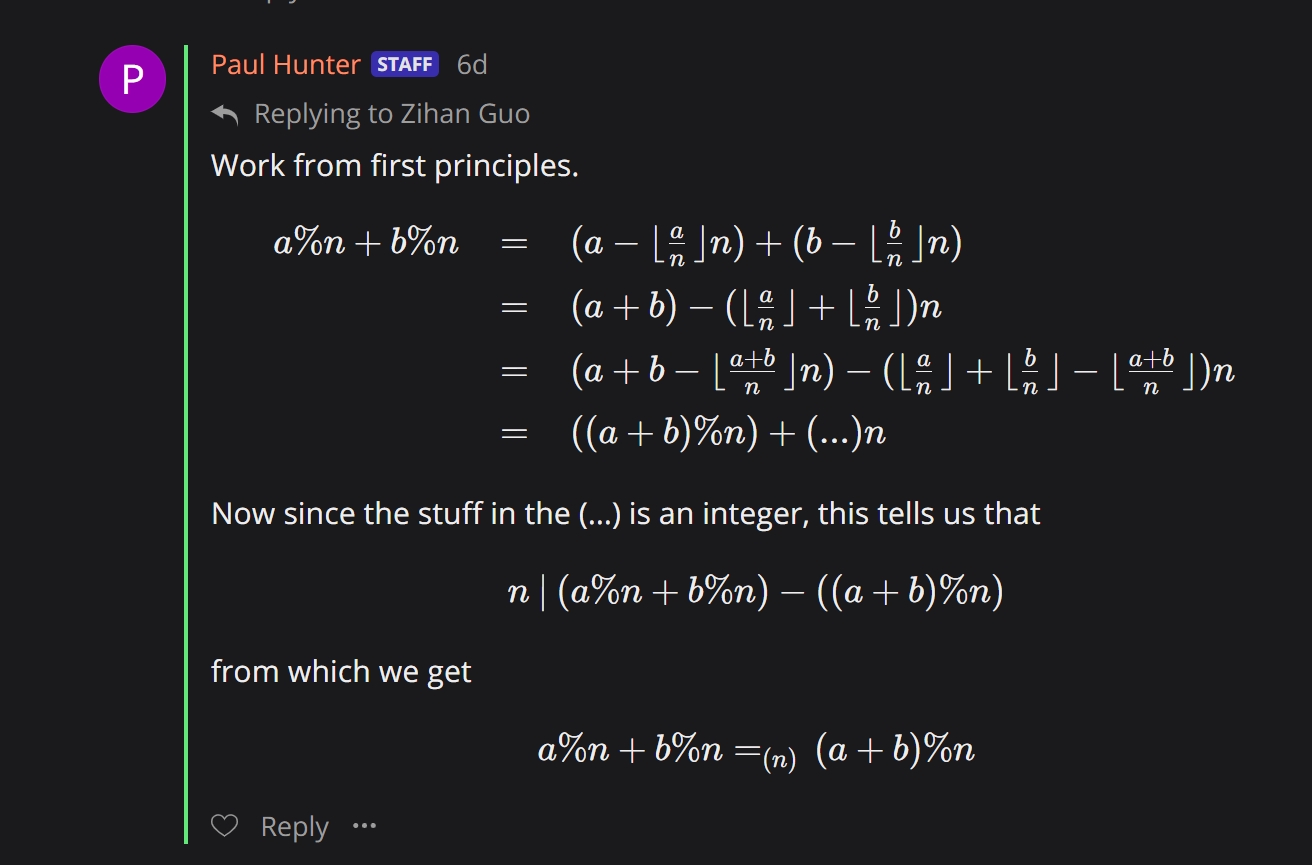
Here is Paul Hunter’s proof, he used the first principle and definition to prove the formula:
大数求余
先说下大数求余,从1次方开始向N次方推,直到找到余数为1,则是一个循环。
如下的10的n次方,从10^1算到10^6%6=1,因为算到1,左右再乘10^1=3 (mod 7),会发现就开始循环了。因此,要找到余数为1的那个次方比如这里是6个数发现的,然后直接分解 2021%6=5,直接找第五个数(同10^5%7)得到5
10^2021 % 7 = ?


What is the last digit of $7^{2023}$?

Question:n = abcd is divisible by 9 if and only if the digit sum a + b +c+d is divisible by 9
Show that the 4 digit number n = abcd is divisible by 9
if and only if the digit sum a + b +c+d is divisible by 9.
n = a*10^3+b*10^2+c*10+d (mod 9)
= a*1 + b*1 + c*1 + d (mod 9)
= a+b+c+d (mod 9)
Euclidean Algorithm

Proof multiples of k between n and m (inclusive)(??)
https://edstem.org/au/courses/19133/discussion/2218972
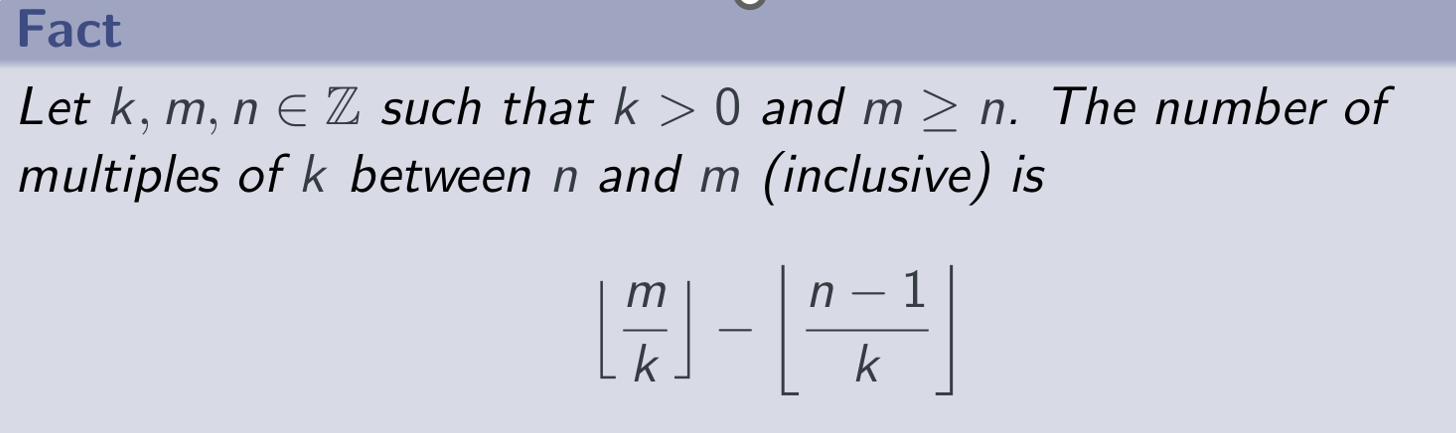
这个题我做到
但是和上图的这个答案还是不太一样,此时我有问题,ED forum上问了下。
(不放我自己的详细笔记了,参考下图tutor的解法)
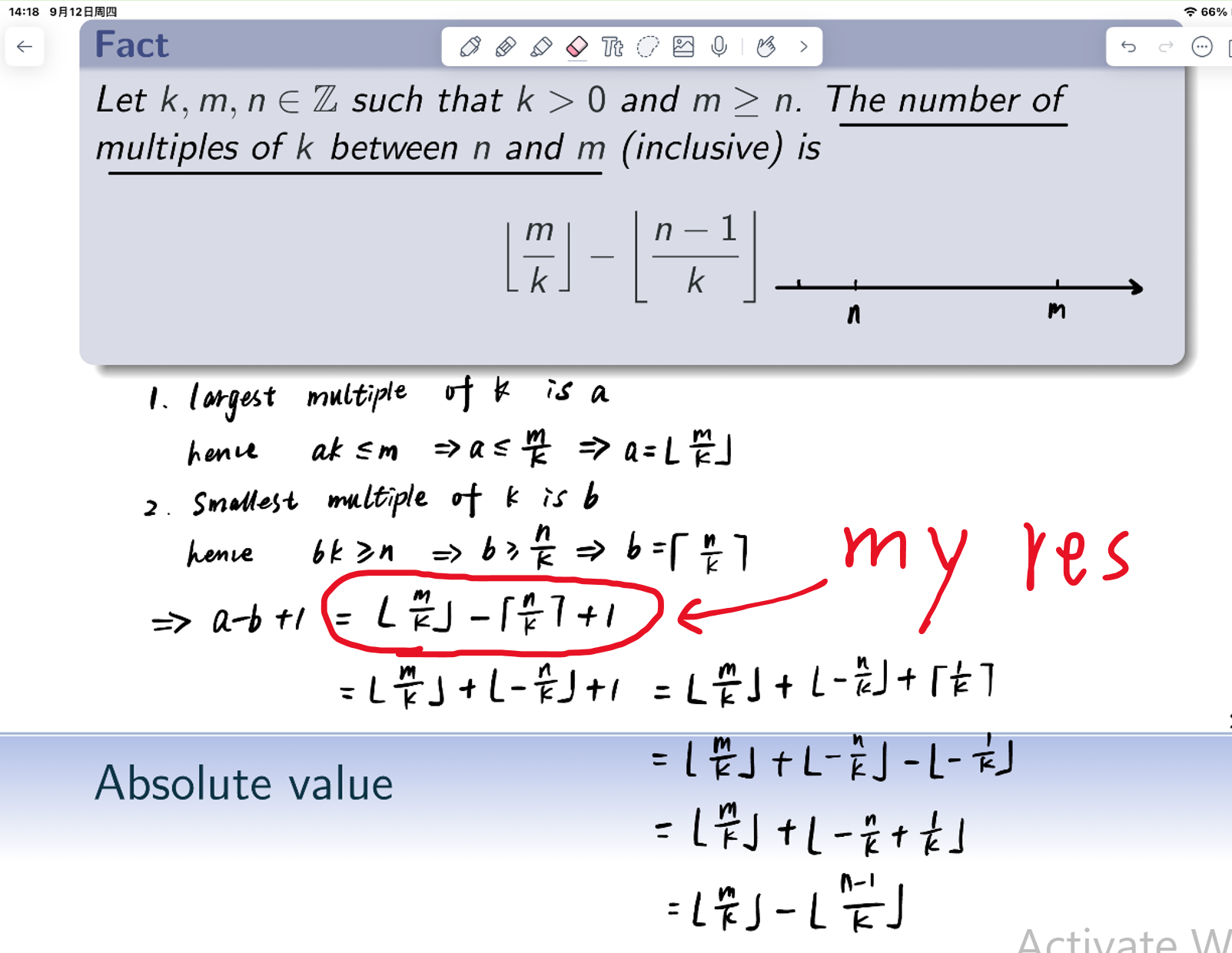
好人之证明:

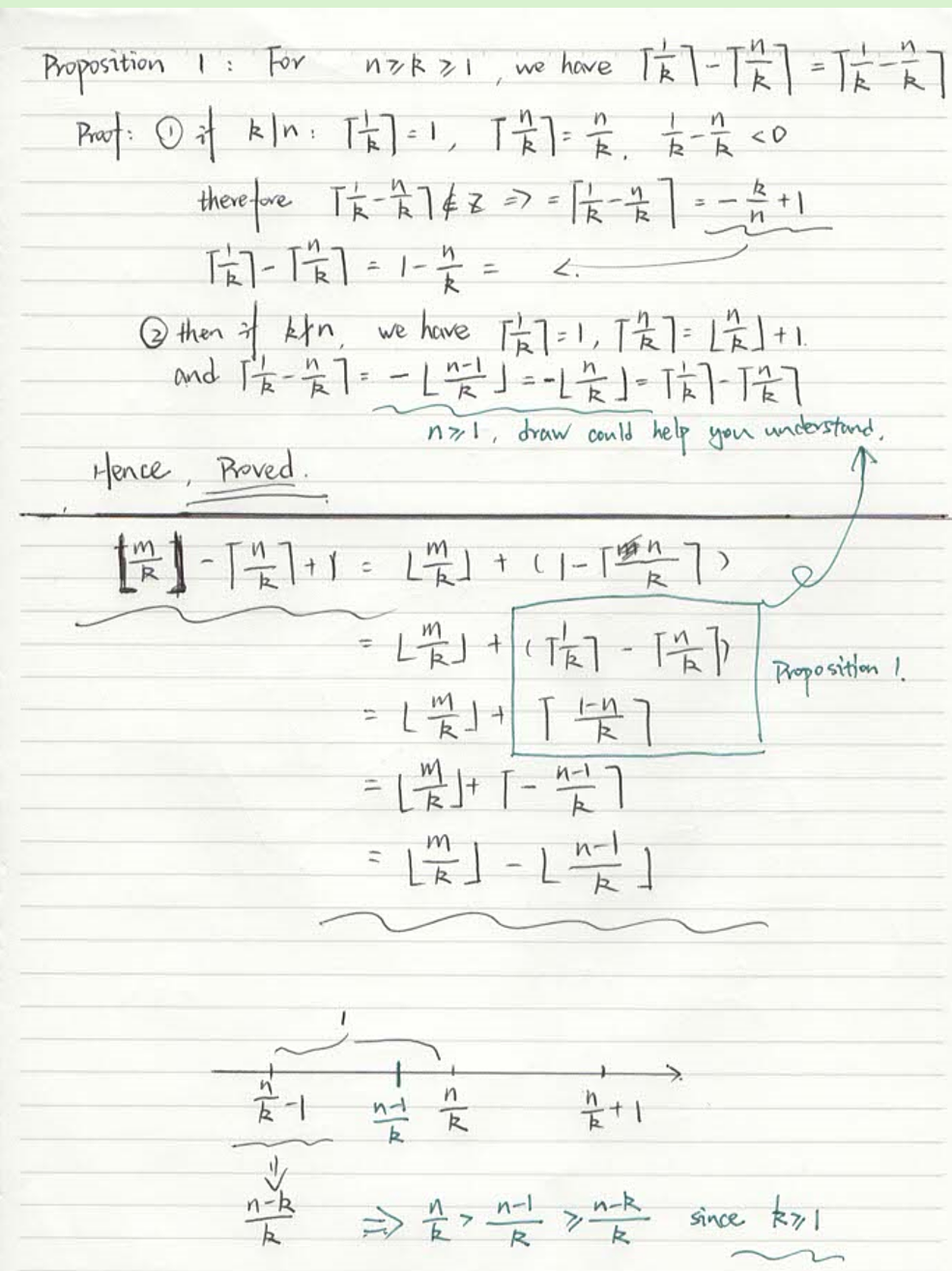
gcd(m,n)lcm(m,n)=|m||n|
关键点:
可以把任何数字,拆分成N个素数的幂的乘积
比如13是 $13=2 \times 5^0 \times 7^0 \times 11^0 \times 13$
提醒下,素数是从2开始的,最小的素数是2


For m,n ∈ Z, if m > n then gcd(m,n) = gcd(m−n,n)

How many numbers between 1 and 653 are divisible by 3 or 5?

1. 算[1,653]中3的倍数的个数
最小是3,最大是651,N(3)=(651-3)/3 + 1 = 217
2. 算5的倍数
the smallest is 5, and the largest # is 650
So N(5)=(650-5)/5 + 1 = 130
3. find the # of the multiples of 15
The smallest is 15, and the largest # is 645
So N(15)=(645-15)/15 + 1 = 43
So we calcute N(3) + N(5) – N(15) = 217+130-43 = 304
Suppose that n is a positive integer. Explain why n and n + 1 are coprime.

Find the last two digits of $7^{7^{7}}$

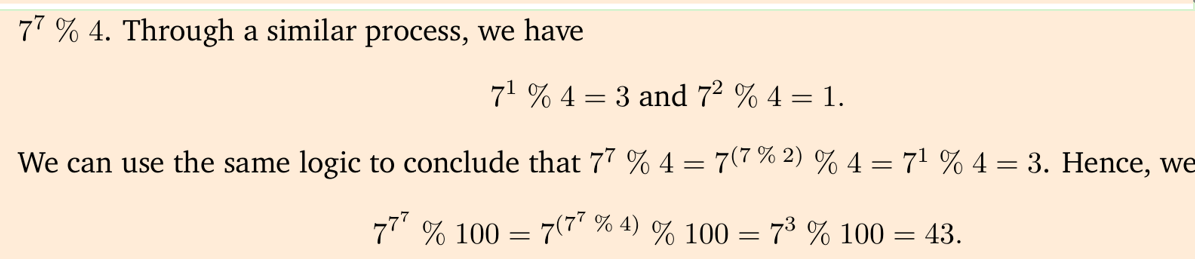
$7^7$ -(4*205885)=3
so it is 43.
Find the least positive integer n for which 5n % 17 = 16. Hence, evaluate 5200 % 17.
巧妙之处在于,考虑到%17时,16=-1,所以-1的平方就是1,这就是一个循环。

Welcome to point out the mistakes and faults!